Oromandibular dystonia is a focal dystonia that manifests as involuntary masticatory andor tongue muscle contractions. TMJ derangement dysfunction.

Lateral Pterygoid Muscle Wikipedia
It can assist in protrusion of the mandible.

. Using the medial and lateral pterygoid muscles as references identify the buccal branch of the mandibular nerve CN V3 and accompanying buccal artery. Lateral pterygoid medial pterygoid. The medial pterygoid is a muscle of your temporomandibular joint and can cause pain in the jaw throat and ear if it is tense or carries trigger points.
Three of them masseter temporalis and medial pterygoid are powerful closers of the joint and account for the strenth of the bite. The superior part arises from the lower part of the lateral surface of the. Pain Trigger Points.
Authors Yunn Jy Chen 1 Pei-Hsuan Chang 2 Ke-Vin Chang 3 Wei-Ting Wu 4 Levent Özçakar 5 Affiliations 1 Department of Dentistry School of. Musculus pterygoideus lateralis is a thick and short triangular-shaped muscle located in the infratemporal fossa of the skull. The primary action is to elevate the mandible and.
Although many temporomandibular joint TMJ symptoms can be alleviated by pterygoid work other structures and patterns will almost always need to be addressed as well. These four muscles move the mandible and are involved in chewing. It is classified as one of the primary muscles of mastication.
The outer surface of the muscle lies against the inner surface of mandible from which it is separated by the lateral pterygoid muscle sphenomandibular ligament maxillary artery mandibular nerve and its. It belongs to the group of masticatory muscles along with the lateral pterygoid masseter and temporal muscles. Lateral pterygoid is the only masticatory muscle which opens the mouth.
The lateral pterygoid muscle is composed of two heads - superior and inferior. Medial pterygoid muscle consists of two heads. Acting together with the lateral pterygoid muscles they protrude the mandible which is important in the grinding movement of mastication.
The smaller superficial head has its origin mainly from the maxillary tuberosity with some fibers arising from the pyramidal process of the palatine bone. On this page you will find instructions how to do this. Attachments of Medial Pterygoid Muscle.
Pterygoid branches of the maxillary artery. An upper superior and a lower inferior. The lateral pterygoid is a short thick muscle somewhat conical in form which extends almost horizontally posteriorly and laterally between the infratemporal fossa and the condyle of the mandible.
The nerve and artery usually pass between the two heads of the lateral pterygoid muscle. The medial pterygoid muscle attaches to the angle of the mandible and to the lateral pterygoid plate to form a sling with the masseter muscle that suspends the mandible Figure 6-19. The medial and lateral pterygoids move the.
Deep head - medial surface of the lateral pterygoid plate sphenoid bone Insertion. The medial pterygoid can be v. Ultrasound Guided Injection for Medial and Lateral Pterygoid Muscles.
These two nerves pass between the medial and lateral pterygoid muscles. The lateral pterygoid Latin. The medial pterygoid muscle has a superficial and a deep head which arise from different areas of the jaw.
For example it is essential to assess and balance the effect of the masseters temporalis digastrics and superficial cervical fascia. The arterial supply to medial pterygoid muscle is from the pterygoid branches of the maxillary artery. Bilateral contractions - push the mandible forward elevate the mandible.
The medial pterygoid is a thick quadrilateral muscle. The medial pterygoid acts together with masseter to elevate the mandible. Lateral Pterygoid this muscle lives directly behind your upper back molar using the same-sided hand ie right hand for right pterygoid with your palm against your cheek place your pinky inside your cheek on the row of upper teeth your jaw can rest closed once.
Superficial head - maxillary tuberosity of the maxilla pyramidal process of the palatine bone. Protrusion elevation medial movement of mandible. On the medial side deep surface the muscle is related to the mandibular nerve the middle meningeal artery the sphenomandibular ligament and the upper part of the medial pterygoid muscle.
Include SCM masseter medial pterygoid lateral pterygoids antagonists the contralateral pterygoids ipsilateral masseter temporalis. A Novel Treatment for Orofacial Pain Med Ultrason. The medial pterygoid nerve is a main trunk from the mandibular nerve before the division of the trigeminal nerve - this is unlike the lateral pterygoid muscle and all other muscles of mastication which are supplied by the anterior division of the mandibular nerve.
It has a second slip of origin from the lateral surfaces of the pyramidal process of the palatine and tuberosity of the maxilla. The medial pterygoid muscle attaches to the angle of the mandible and to the lateral pterygoid plate to form a sling with the masseter muscle that suspends the mandible Figure 6-19. Protrusion depression medial movement of mandible.
The medial and lateral pterygoids. However its possible to eliminate these points and tensions with a self-massage. Medial surface of ramus and angle of mandible.
Developmentally the articular disc of temporomandibular joint is a part of tendon of lateral pterygoid muscle. The lower head of lateral pterygoid travels in the middle of the two heads of the medial pterygoid muscle. Posture head position are of considerable importance for all masticatory muscles.
It arises from the medial surface of the lateral pterygoid plate and the grooved surface of the pyramidal process of the palatine bone. Pterygoid tuberosity of the mandible medial surface of the mandibular ramus. Should be considered when pain presents in the region of the joint.
It arises by two heads. Medial surface of lateral pterygoid plate and palatine bone. Medial pterygoid muscle is located in the infratemporal fossa lying deep to masseter and temporalis muscles and medial to lateral pterygoid muscle.
The primary action is to elevate the mandible and laterally deviate it to the opposite side. On the lateral side superficial surface the lateral pterygoid muscle relates to the mandibular ramus maxillary artery temporalis tendon and the masseter muscle. Jaw opening jaw deviation and jaw protrusion types of oromamdibular dystonia are caused by involuntary contraction of the lateral pterygoid muscles.
Medial and Lateral Pterygoids are both well hidden by the lower jaw bone. The lateral pterygoid muscle via its lower head separates the two distinct heads. Medial pterygoid is a thick quadrilateral muscle that connects the mandible with maxilla sphenoid and palatine bones.
Branches of the mandibular division of the trigeminal nerve CN V3 Blood supply. The medial pterygoid muscle causes pain in the temporomandibular joint and the ear which increases when you bite down on something. The pterygoids are often weak and inactive due to the underdevelopment of the maxilla which causes occlusion to establish too posteriorlyThe pterygoids pro.
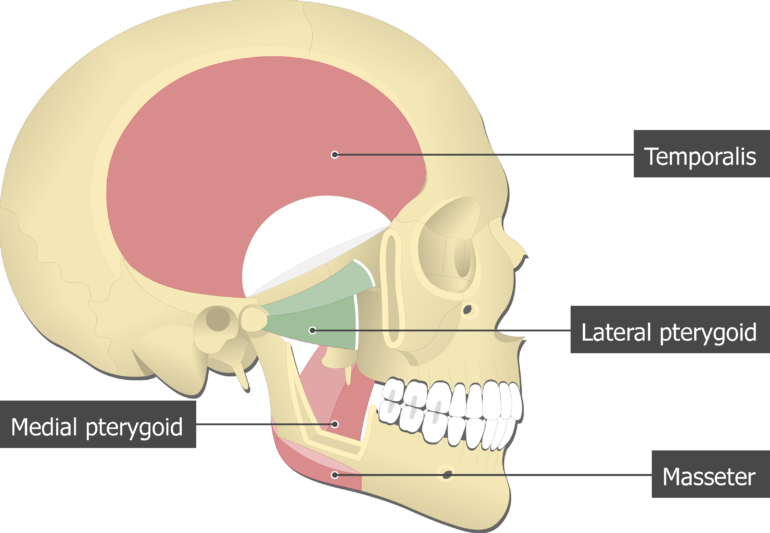
Lateral Pterygoid Muscle Attachments Actions Innervation
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/14110/Pterygoid_muscles.png)
Medial And Lateral Pterygoid Muscle Anatomy And Function Kenhub
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/14112/IjxD1w7xmfmSR4xC7FugCQ_Pterygoideus_lateralis_02.png)
Medial And Lateral Pterygoid Muscle Anatomy And Function Kenhub

Lateral Pterygoid Muscle Wikipedia
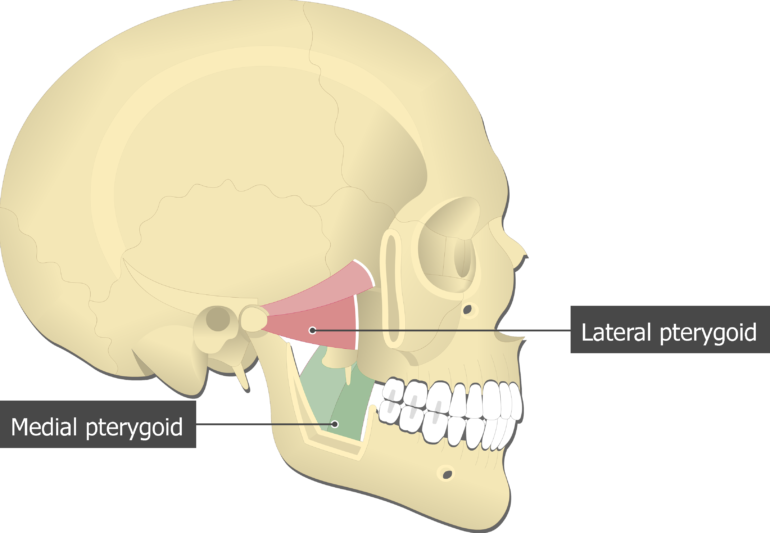
Medial Pterygoid Muscle Attachments Actions Innervation
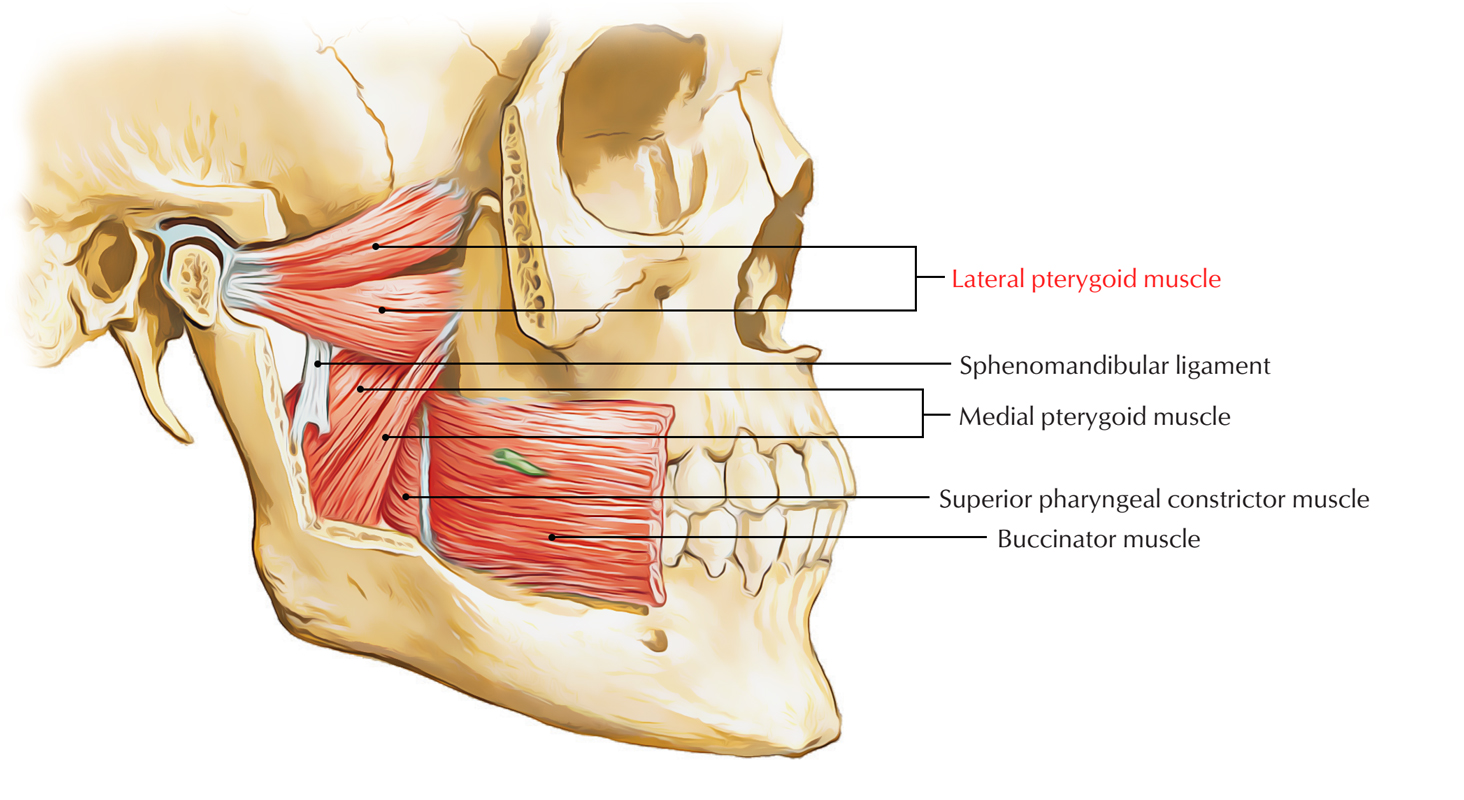
Lateral Pterygoid Muscle Earth S Lab

Medial Pterygoid Learn Muscles
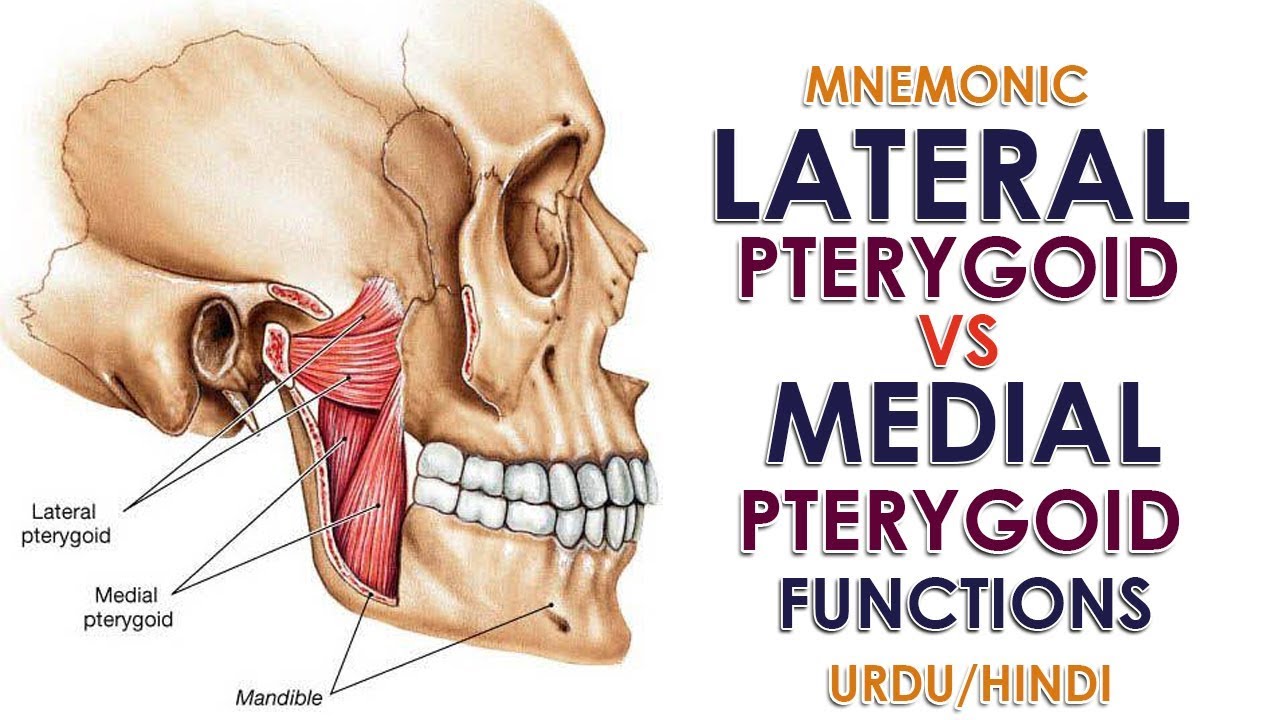
Mnemonic Lateral Pterygoid Vs Medial Pterygoid Function Urdu Hindi Youtube
0 comments
Post a Comment